The Official GA4 Implementation Checklist Of “Hidden” Things You Absolutely Need
Any marketer in the digital community has groaned hard at least five times over GA4 migration in the past year. Those groans are unlikely to go away anytime soon. In fact, you may want to have your earbuds in over the next few months when the transition officially comes to pass.
You can find how to migrate your GA4 with the help of Tag Manager in many places across the web. But there are important tasks during this migration that you must know about — that Google might not explicitly tell you. Use this checklist to mark off these boxes before you rest easy, and read more below.
Here’s the Positive Pete angle: Any transition is hard to make. Like learning Google Analytics, you were better at it in year two than year one, and so on. This will be the case with GA4 migration. As bugs get fixed and new features implemented, we will all settle in (I can remember my first time looking at it, noticing the absence of the Landing Page report and getting queasy — it has since been added).
We’re in the middle of it now, so here’s what you need to know to make your transition as seamless as possible to ensure your data is not missing.
What Are The Basics of GA4 Implementation?
BAM’s digital team has migrated over 100 websites from Universal Analytics to GA4. This includes utilizing Google Tag Manager to create the proper configuration, conversion tracking, and implementing to third party applications such as Call Tracking Metrics and Scheduling Applications. We will assume that you understand how to complete a basic setup. Google has tools in place to guide you through this process, and if you wait until July, it will do it for you automatically (though you would want to start collecting data as soon as possible).
Each follows this basic step:
- Setting Up GA4: By now, attempting to access your dashboard will force a pop-up that practically begs you to create a GA4 account. This is simple and a the platform will automatically create one for you at the click of a button.
- Configure in Google Tag Manager (GTM): Ensuring GA4 is streaming data by configuring your Google Tag Manager account is integral. First, you must find your measurement ID, which can either be searched for, or found in the “Data Streams” section of your dashboard.
- Create A Variable: Assuming you have Google Tag Manager script installed in your site, access the GTM platform and create a new variable. Make it a “Constant” and the value the Measurement ID (G-xxxxxxxx)
- Create a GA4 Pageview Tag with this Variable, and select “All Pageviews” as the trigger.
- Test your page with the Preview Debug mode and make sure it is firing
Read more about GA4 setup in Google Tag Manager here.
Important Tasks During The GA4 Migration You MUST Know That Google Does Not Explicitly Tell You
After completing the above steps, ask yourself these questions:
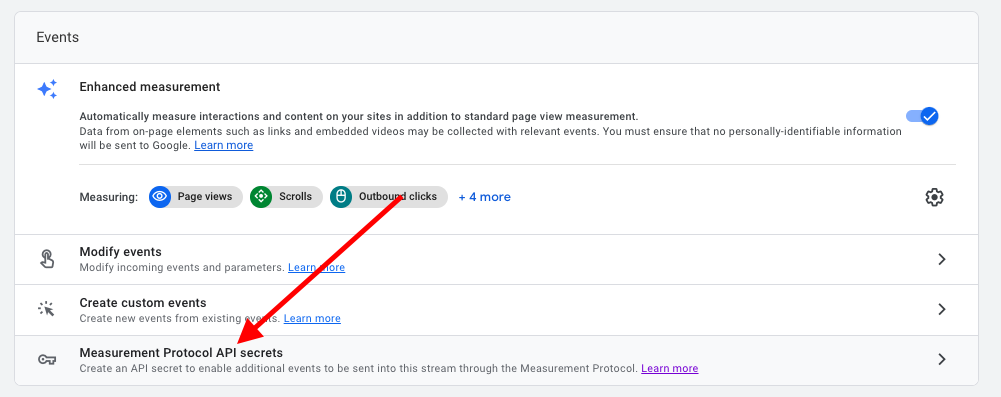
API Secrets: Do I have conversion tracking connected to a third party, such as a scheduler application or call tracking?
This will require an “API Secret” to be created. Your third party should have built out a GA4 integration to connect to the API Secret (you can name it whatever you want).
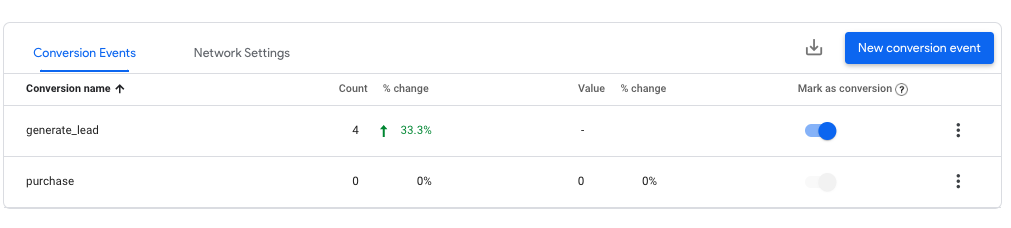
Do I track specific lead form submissions?
Google has a basic form submission (and phone call) tracking tool built in, but we highly suggest creating your own conversions and customizing them based on form type, or “thank you page” path. New conversions can be set up in Google Tag Manager.
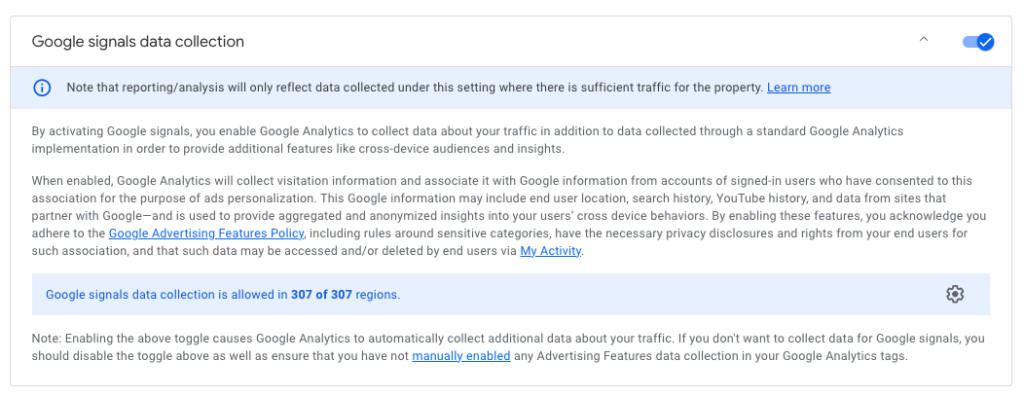
Do I run any paid advertising with Google?
If you do, or plan to in the future, you’ll need to turn on “Google Signals” in the data settings. Be leery if you use server-side tracking, though. Learn more here.
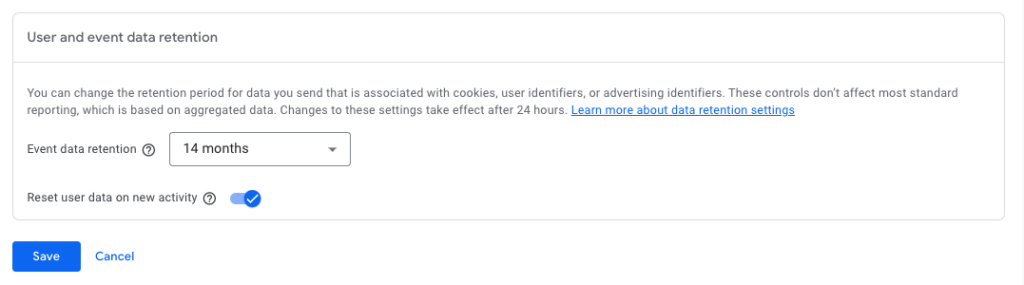
Do I want to retain more than two months worth of data?
A default GA4 profile has the data retention window set to two months — ridiculous! Anyone wanting a piece of year over year data will have to go into data retention and change it to the maximum 14 months.
Do I want to track more than 14 months of data?
Piggybacking off the last question, if you want to warehouse your data longer than that you’ll need BigQuery. The first steps in doing this are to go into your Google Cloud Console and create a project. Make sure billing is enabled! Then, go back into GA4 and create a BigQuery link. OptimizeSmart has a detailed post on this here.
Understand How The GA4 Model Is Different
The GA4 Model is different in both data structure and user interface, among other things.
Data Structure in GA4 versus Google Analytics
The data structure in GA4 differs from the older Universal Analytics (UA) version. Here are a few key differences:
- Event-based tracking: GA4 focuses on event-based tracking, where events represent specific user interactions on your website or app. Events can include button clicks, form submissions, video plays, and more. This event-based approach provides more flexibility in tracking and analyzing user behavior.
- Enhanced measurement of user interactions: GA4 introduces automatic event tracking for common user interactions, such as page views, scrolls, outbound clicks, and file downloads. This means that you don’t have to manually set up tracking for these interactions as you did in UA. GA4 automatically collects this data, providing a more comprehensive view of user engagement.
- Simplified data model: GA4 simplifies the data model by organizing data into four main components: events, parameters, user properties, and user interactions. Events represent user actions, parameters provide additional details about events, user properties describe characteristics of users, and user interactions represent the touchpoints users have with your business. This streamlined data model allows for more flexibility and scalability.
- Focus on users instead of sessions: In UA, the primary unit of analysis is a session, which represents a user’s visit to your website within a specified timeframe. In GA4, the focus shifts to users, providing a more holistic view of user behavior across multiple sessions and devices. This allows for better understanding of user journeys and engagement over time.
- AI-powered insights: GA4 leverages Google’s advanced machine learning capabilities to provide valuable insights automatically. It can generate predictive metrics, segment users based on their behavior, and even suggest actions to optimize marketing efforts. This AI-driven approach helps marketers gain deeper insights without extensive manual analysis.
These are just a few of the key differences in the data structure between GA4 and UA. It’s important to note that GA4 represents a significant shift in how data is collected, organized, and analyzed. Understanding these differences will help marketers leverage the full potential of GA4 and make informed decisions based on the new data structure.
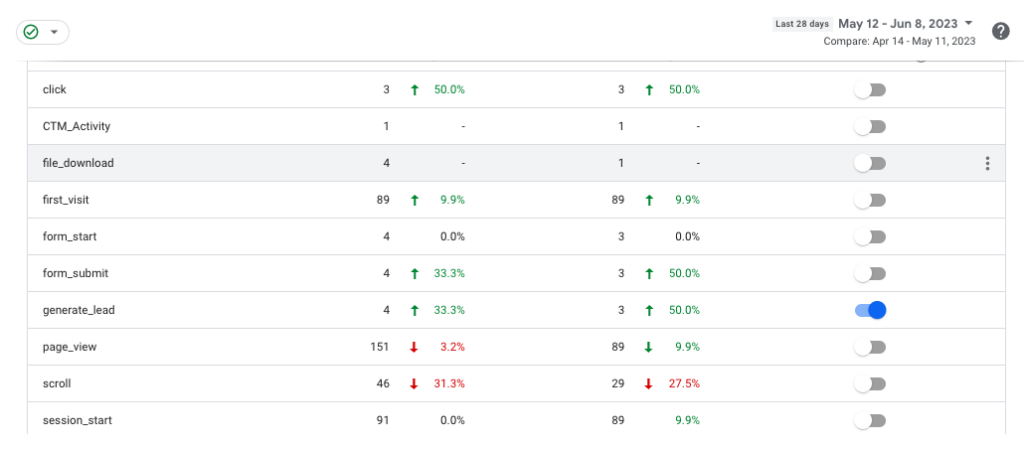
The GA4 User Interface Vs. Google Analytics
The user interface (UI) in GA4 has undergone significant changes compared to the older Universal Analytics (UA) version. Here are some key differences you’ll notice in the GA4 user interface:
Home Screen: When you log in to your GA4 account, the Home screen provides a high-level overview of your website’s performance. It includes metrics like active users, engagement, and conversion rate. The Home screen also highlights important insights and trends to help you quickly understand the key aspects of your data.
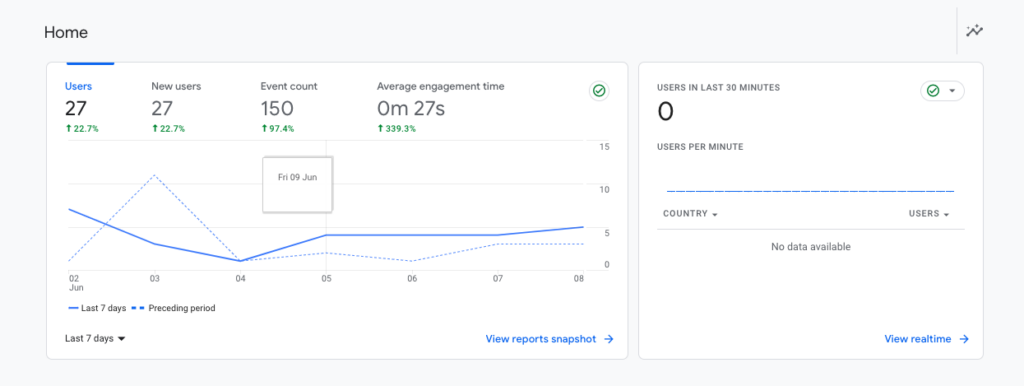
Navigation: The navigation in GA4 has been restructured for a more streamlined experience. Instead of the traditional left-hand menu in UA, GA4 uses a simplified top menu with fewer categories. The main sections include Analysis, Real-time, Explore, and Admin. Each section offers specific reports and tools to analyze your data.
Explorations: Explorations is a powerful feature in GA4 that allows you to create custom reports and perform in-depth analysis. It provides a wide range of analysis techniques, such as exploration, funnels, cohorts, and segments. The Analysis Hub offers a more intuitive and flexible approach to analyzing your data compared to the older UA interface.
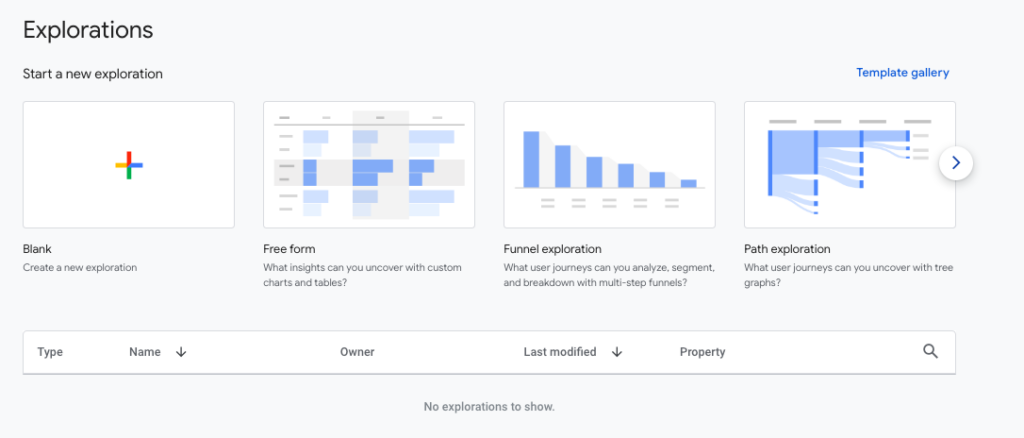
Insights: GA4 introduces the Insights section, which leverages Google’s machine learning capabilities to automatically surface valuable insights from your data. It highlights significant trends, anomalies, and opportunities for optimization. Insights provide actionable recommendations to improve your marketing strategies based on data patterns and trends.
Reports: The reporting interface in GA4 offers a fresh look and feel compared to UA. Reports are more visually appealing, with improved visualization options, charts, and graphs. GA4 also includes pre-built reports, such as engagement, acquisition, and user behavior, which provide quick access to key metrics and dimensions.
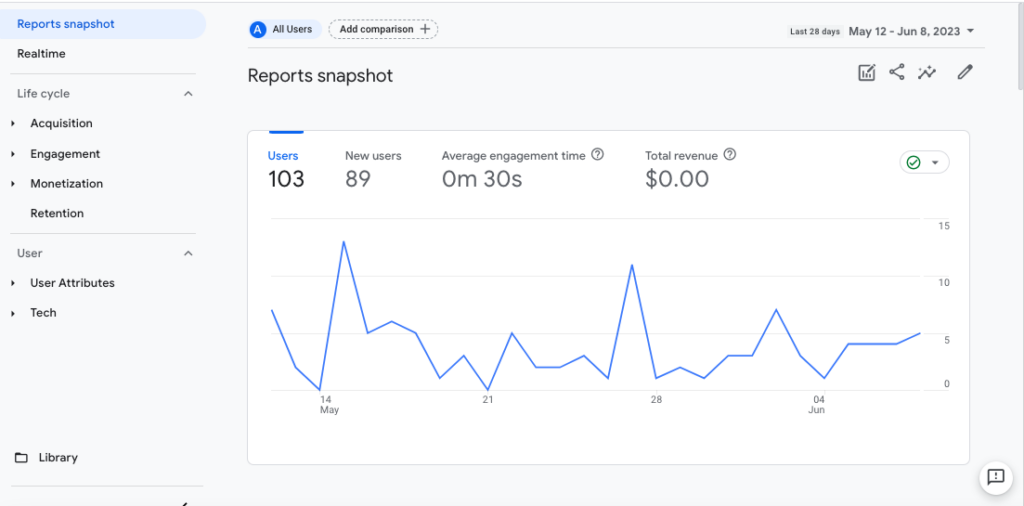
Enhanced Customization: GA4 provides more customization options for reports and dashboards. You can create custom metrics, dimensions, and segments based on your specific business needs. The enhanced customization capabilities allow you to tailor the analytics experience to your unique requirements and gain deeper insights into your data.
Real-time Monitoring: GA4 emphasizes real-time data monitoring. The Real-time section provides up-to-the-minute information on active users, events, and conversions happening on your website or app. This feature enables you to monitor live campaigns, events, or sudden spikes in traffic in real-time.
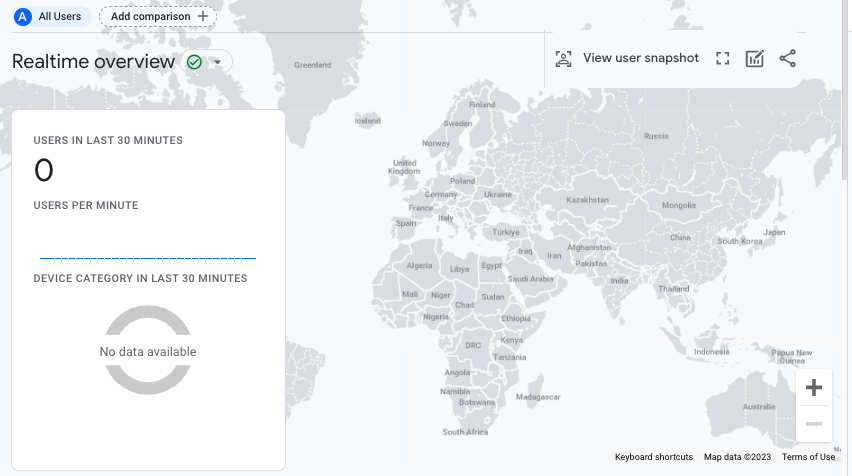
These are some of the notable differences you’ll encounter in the GA4 user interface. The overall aim is to provide a more user-friendly, intuitive, and insightful experience for marketers and analysts, allowing them to navigate and analyze data more efficiently and make data-driven decisions.
Other Major Differences Between GA4 Migration and Universal Analytics to Consider
In addition to differences in data structure and user interface, here are a few other notable distinctions between GA4 and the older Universal Analytics (UA) version:
- Cross-Platform Tracking: GA4 is designed to provide a more comprehensive view of user interactions across various platforms and devices. It supports cross-platform tracking, allowing you to track user behavior across websites, mobile apps, and even offline interactions. This enables a more complete understanding of user journeys and engagement across multiple touchpoints.
- Enhanced Privacy and Compliance: Privacy and compliance have become increasingly important in the digital landscape. GA4 incorporates privacy-centric features to align with evolving regulations and user expectations. It includes options to easily configure data retention periods, manage data subject consent, and enables more granular control over data collection and sharing.
- Focus on Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics: GA4 heavily leverages machine learning and predictive analytics to provide valuable insights and automation capabilities. It utilizes AI-powered models to generate predictive metrics, such as churn probability and revenue forecasts. Additionally, GA4’s machine learning algorithms assist in data analysis, anomaly detection, and user segmentation for more accurate targeting and personalization.
- Event-Based Funnel Analysis: GA4 introduces a new approach to funnel analysis. Instead of relying solely on page views, GA4 allows you to define custom conversion events and build event-based funnels. This provides more flexibility in analyzing and optimizing user flows and conversion paths, beyond traditional page-based funnels.
- Deeper Integration with Google Ads: GA4 offers deeper integration with Google Ads, enabling a more seamless connection between your analytics and advertising data. You can import Google Ads campaigns and cost data directly into GA4, allowing you to evaluate the performance of your ad campaigns alongside other engagement and conversion metrics.
- Simpler Configuration and Tagging: GA4 simplifies the configuration process by introducing a unified tagging system called the Google Tag Manager. It provides a streamlined approach to managing tags, such as tracking codes and event triggers, across various platforms. This simplification enhances implementation efficiency and reduces dependency on developers.
Reporting With GA4 In Looker Studio
Having good data is often not enough — it has to face properly externally. Many clients, including BAM, use, build and implement Looker Studio reports for our dashboards.
Connecting your GA4 property to looker studio is similar to Universal Analytics — the only issue is that since the data structure is different in GA4, there is no quick way around reworking your current looker studio reports.
Connect your GA4 property to Looker Studio. Follow Looker’s instructions and enter the Measurement ID in the Looker Studio configuration settings.
Once the connection is established, you can use Looker Studio’s features to explore and analyze your GA4 data. Create custom reports, dashboards, and leverage filtering and segmentation options to gain insights.
Supermetrics has a great guide for this, and also offers custom dashboard templates. There is only a handful of free templates housed within looker studio for GA4 right now, but that number is likely to grow.
It’s important to note that GA4 is still evolving, and new features and enhancements may be introduced over time. As Google continues to develop GA4, it’s advisable to stay updated with the latest releases and documentation to fully leverage its capabilities and stay ahead in data-driven marketing.

